📓 Earth's Structure: Layers of the Earth, rocks, and minerals
Posted by Admin Last Updated on Saturday, 15 February 2025 Under Class - 5 ScienceEarth's Structure: Layers of the Earth, rocks, and minerals
Detailed overview of Earth's structure:

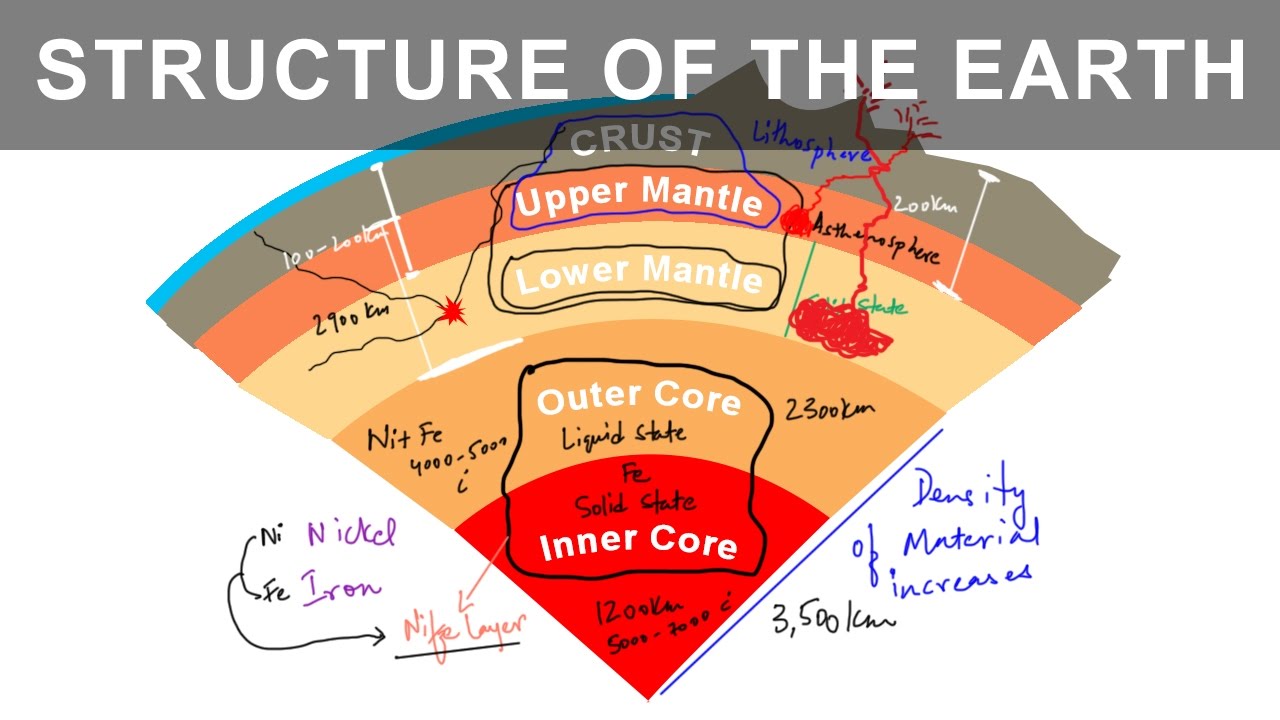
Layers of the Earth
1. Crust: The outermost layer, ranging in thickness from 5-70 km.
2. Mantle: The thick, viscous layer beneath the crust, extending from 35 km to 2,900 km in depth.
3. Outer Core: A liquid layer of iron and nickel, approximately 2,250 km thick.
4. Inner Core: A solid, iron-nickel alloy at the center of the Earth, with a radius of about 1,220 km.
Rocks
1. Igneous Rocks: Formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava (e.g., granite, basalt).
2. Sedimentary Rocks: Formed from the accumulation and compression of sediments (e.g., sandstone, limestone).
3. Metamorphic Rocks: Formed through the transformation of existing rocks under high pressure and temperature (e.g., marble, slate).
Minerals
1. Definition: Naturally occurring inorganic substances with a specific chemical composition and crystal structure.
2. Types:
1. Silicates (e.g., quartz, feldspar)
2. Oxides (e.g., iron oxide, titanium oxide)
3. Carbonates (e.g., calcite, dolomite)
3. Importance: Minerals are essential for many industrial processes, construction materials, and electronic devices.
Key Concepts
1. Plate Tectonics: The theory that the Earth's crust is divided into moving plates that interact at their boundaries.
2. Geologic Cycle: The continuous process of rock formation, transformation, and destruction.
3. Weathering and Erosion: The breakdown and removal of rocks through exposure to wind, water, ice, and temperature fluctuations.
Examples and Applications
1. Natural Resources: Understanding Earth's structure and composition helps locate and extract natural resources, such as minerals, fossil fuels, and water.
2. Geotechnical Engineering: Knowledge of Earth's structure informs the design and construction of buildings, bridges, tunnels, and other infrastructure projects.
3. Environmental Monitoring: Studying Earth's structure and processes helps track climate change, predict natural hazards, and monitor environmental health.
See Topics - Class - 5 - Science - Read in Hindi Download in Word